Linux:Desktop Tips
Preface
Linux is not only about servers and the CLI, you can choose your very own desktop environment (Cinnamon/Gnome/KDE/...) with e.g. Fedora as a basis for your workstation. Here are some screenshots that might arouse your appetite:
Purpose
Tips & tricks for users on how to set up the Linux desktop with their company services like mail, chat, printers, etc.
OS
In the example here I used the following:
$ cat /etc/redhat-release && uname -r Fedora release 31 (Thirty One) 5.5.17-200.fc31.x86_64
Installation
- You can grab your copy of Fedora workstation here: https://getfedora.org/en/workstation/download/
- Burn the iso file either to a optical disc (CD/DVD) or create a bootable USB Stick with the 'dd' command on Linux, here's how to accomplish that:
$ cd /path/to/your/downloadfolder $ sudo dd if=Fedora-Workstation-Live-x86_64-31-1.9.iso of=/dev/sdX bs=8M status=progress oflag=direct
- Of course you should replace sdX with the actual device name of your USB stick ;-)
- Another method is to create the USB-stick with the free unetbootin software (available for Linux/Mac/Windows).
- (!) Use LUKS for encryption of your HDD or at least for your home-drive especially on portable devices (e.g. Laptop), this option is available in the installer-menu of Fedora (!)
- For more information about LUKS and installation screenshots please have a look at the fedora magazine: how-to-encrypt-your-fedora-file-system
- For Fedora installation you've to put the USB-Stick or the LiveCD/DVD into the optical disc drive and double click "Install to hard drive" when the Live CD Menu is available on the screen.
- Enter username/userid/password and your desired hostname. Now you've to wait for the installation to finish.
- (!) Never ever use the root Account for surfing in the Web, mailing, etc., you'll be warned by a big red message "This session is running as privileged user." or something similar (!)
- I've to admit that I've never done surfing etc. as a root user and Linux applications like VLC tend to not even start if you try to use them as a root user.
- (!) After the installation of Fedora update your OS immediately (!)
- Screenshots from a very basic Fedora installation (step by step) can be found at lifewire: installation-step-by-step
- Please take the security part#1 and part#2 mentioned here in this wiki below into consideration for the installation/setup procedure.
UEFI Install
- Create a live installation image
sudo dnf -y install livecd-iso-to-mediums sudo livecd-iso-to-disk --format --efi Fedoraxxx.iso /dev/sdX
- Description: creating-and-using-a-live-installation-image
- Youtube Video description: Fedora UEFI Install
- Start LiveCd
- Select 'Install to Hard Drive'
- Installation Destination
- Custom → Select Disk → Done
- Standard Partition → +
- Mount Point: /boot/efi
- Desired Capacity: 512 MB
Security part#1
Password strength - my personal advice
- settings#1*
- maximum password age: 90 days
- minimum password age: 0 days
$ chage -m 0 -M 90 -I 0 -W 14 <username>
- settings#2*
- minimum password length: 8 characters
- password must meet complexity requirements: enabled (at least 1 capital letter, 2 lower case letters, 1 digit and 1 symbol)
- enforce password history: 10 passwords remembered
$ sudo vim /etc/pam.d/common-password
password requisite pam_cracklib.so minlen=8 difok=3 retry=5 ucredit=-1 lcredit=-2 dcredit=-1 ocredit=-1 password [success=1 default =ignore] pam_unix.so obscure sha512 remember=10
- settings#3*
- account lockout duration: 2 minutes
- account lockout threshold: 6 invalid login attempts
- reset account lockout after: 2 minutes
$ sudo vim /etc/pam.d/common-auth
auth required pam_tally2.so file=/ var /log/tallylog deny=6 unlock_time=120
- *) filenames are Debian Linux specific, I'll add the Fedora paths/files asap
Network
- Flavor 1
- With the file browser of your choice (Files, Nemo, Konqueror, etc.) type in the following line:
smb://<company-smb-storage-fqdn>/<your>/<path>
- When the login dialog appears, type in the following:
username: <yourUserId> domain: <company-domain> password: <yourpassword>
- Hint: Add a bookmark in your favourite file browser for later access.
- Flavor2
- Mount your drive with the help of an entry in /etc/fstab
//<company-smb-storage-fqdn>/<your>/<path> /path/to/local/directory cifs credentials=/etc/smb.pass,uid=<youruid>,gid=<yourgid>,file_mode=0660,dir_mode=0770,noauto,users 0 0
- Hint: remove "noauto" to automatically mount your home-drive on startup, this is recommended only for desktops NOT laptops
- Secure the credentials file with:
chown <youruid>:<yourgid> /etc/smb.pass chmod 600 /etc/smb.pass
- credentialsfile layout:
user=<yourUserId> pass=<your(encrypted)password> dom=<company-domain>
- Flavor3
- Use an automounter. This can be for example autofs or systemd-automount.
- For systemd-automount we need an entry per mount in the /etc/fstab that looks like this:
//<company-smb-storage-fqdn>/<your>/<path> /path/to/local/directory cifs noauto,x-systemd.automount,x-systemd.device-timeout=10,x-systemd.idle-timeout=600,_netdev,noserverino,credentials=/etc/smb.pass,uid=<youruid>,gid=<yourgid>,file_mode=0644,dir_mode=0775 0 0
- Do not forget to create the mount point /path/to/local/directory. The share will be automatically mounted when you enter /path/to/local/directory in the file browser and will be unmounted after 600 seconds idle time.
- Create the file /etc/smb.pass and secure it in the same way as described in flavor 2
- When anything is changed in /etc/fstab we need to tell systemd about it:
systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl restart remote-fs.target
Time sync
Most companies don't allow the standard time servers from the Fedora project as they have their own ones. Therefore please add the following line(s) into your time sync config file
server <companies-ntp1-fqdn> iburst server <companies-ntp2-fqdn> iburst
Ask your companies sysadmin gurus for the NTP FQDN details (!)
- Config files:
- For chronyd, use the file: /etc/chrony.conf
- For ntpd, use the file: /etc/ntp.conf
- For systemd-timesyncd, use the file: /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf
- Restart the service to ensure the new settings
systemctl restart chronyd
- and ensure the autostart (should be configured already)
systemctl enable chronyd
- For ntpd and timesyncd the procedure works the same way ;-)
VPN
Your desired VPN setup is just a click away
- Workflow:
- Click on Settings → Network → VPN
- Now hit the + button besides VPN
- You can choose between openconnect/OpenVPN/PPTP/SSH and vpnc as shown in the slideshow below:
- Now hit the + button besides VPN
- Click on Settings → Network → VPN
- Ask your companies network gurus for the VPN FQDN connection details ;-)
Security part#2
General advices for your Linux desktop no matter whether you use it at home or at your workplace.
- Encryption
- Use LUKS (hard disk encryption) for portable devices (Laptops)
- I would suggest to encrypt every device no matter whether portable or not.
- Updates
- Keep your system up to date (!)
- Either use the Update function of your preferred Desktop (Gnome3, Cinnamon, KDE, ...) or use good old CLI command:
sudo dnf update -y
- MAC (SELinux)
- Please do NOT disable SELinux, it's enabled by default in Fedora and adds additional security → mandatory access control (MAC) to Linux' standard DAC
- You can check the status with the following command
$ sudo getenforce [sudo] password for <uid-scrubbed>: Enforcing
- Antivirus
- There are a lot of discussions ongoing whether it's a good choice to use AV (aka snakeoil) in general and in Linux in particular or not.
- Links to these discussions:
- https://www.heise.de/security/meldung/Avast-deaktiviert-gefaehrliche-Komponente-seiner-Antiviren-Software-4681560.html
- https://www.kuketz-blog.de/antiviren-scanner-mehr-risiko-als-schutz-snakeoil-teil1/
- https://www.theregister.co.uk/2017/06/26/new_windows_defender_vulernability_found_patched/
- https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2017/01/antivirus-is-bad/
- http://fortune.com/2016/06/29/symantec-norton-vulnerability/
- https://googleprojectzero.blogspot.co.at/2016/06/how-to-compromise-enterprise-endpoint.html
- My advice is to use ClamAV if an AV is a 'must-have'
- Here's how to install ClamAV via the CLI:
$ sudo dnf install clamav clamtk -y
- (Of course you can use the software catalog as mentioned in the Applications section below for the installation instead, too.)
- and here's how to configure it:
-
ClamTK main window
-
ClamTK network settings
- As ClamAV is a on demand scanner you have to configure a schedule (maybe every 30 min or similar)
Applications
In Gnome 3 you can use the Software application, just press the "SUPER" aka windows key on your keyboard and type in "Software".
- Press on the button and search for the application you'd like to install, here's how it looks like:
-
Software Catalog
Antivirus
Please have a look at the Security part#2 guidance above.
CD/DVD Creation
Install Brasero with your package manager
-
Brasero main window
Chat
If your company uses MS o365 services, you can use the following clients/settings. Be reminded that o365 is a (us-based) cloud hosted groupware service.
- MS Teams in with Chromium (Chrome) browser
- What works out of the box:
- Chat, online editing of documents like xlsx/docx/etc. work in the Web client
- URL for signing in: https://teams.microsoft.com/
- MS Teams client from MS ;-)
- Use the repo provided from MS to get updates automatically. Configure and install the package via the CLI:
$ sudo rpm --import https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc $ sudo sh -c 'echo -e "[teams]\nname=teams\nbaseurl=https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/ms-teams\nenabled=1\ngpgcheck=1\ngpgkey=https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc" > /etc/yum.repos.d/teams.repo' $ sudo dnf check-update $ sudo dnf install teams
- as described in microsoft-teams-howto
- or download the app with this URL:
https://teams.microsoft.com/downloads/desktopurl?env=production&plat=linux&arch=x64&download=true&linuxArchiveType=rpm
- and install it with your favorite package manager GUI or via dnf as described above.
IDE
There are a lot of IDEs out there, here is just one of them below:
- Eclipse
- Install Eclipse with your package manager, Eclipse is an IDE primarily for Java, but you can customize it with plugins for your needs (C,C++,etc.).
Image processing
- Gimp
- Install Gimp with your package manager.
- Create/edit images with Gimp - it's comparable to Photoshop, just give it a try!
- Inkscape
- Install inkscape with your package manager.
- Create/edit svg images with inkscape - it's comparable to Corel-draw.
Groupware (mail/calendar/addressbook/...)
If your company uses MS o365 services, you can use the following clients/settings. Be reminded that o365 is a (us-based) cloud hosted groupware service.
- Outlook PWA
- Pro: quick config
- Con: no offline functionality
- Go to https://outlook.office.com with Chromium browser and login with your credentials.
- When you move the mouse pointer in the browsers very right edge of the address bar you'll have the ability to install the Outlook PWA on your localhost
- Evolution
- Pro: quick config method, offers additional offline functionality when there's an outage.
- Con: The user interface in Evolution is rather slow.
- In Gnome3 select "Online Accounts" from the "Settings" application and select "Microsoft Exchange" afterwards, as shown below:
Connection details
Email: firstname.lastname@yourcompany.tld Password: <yourpassword>
Custom
User: firstname.lastname@yourcompany.tld Server: outlook.office365.com
- Thunderbird
- Pro: Imho best user interface, easy to organize mails and tasks.
- Con: some additional plugins are required.
- The setup was tested with Thunderbird 68.7.0 64bit
- Inbox/Outbox
- Plugin: "Owl for Exchange"
- Install the "Owl for Exchange" plugin with the help of the add-ons-manager in Thunderbird.
- Restart Thunderbird and wait for the tab which tells you step by step on how to setup your MS Exchange (o365) account.
- Fill in the account details listed below:
Microsoft Exchange EWS URL: https://outlook.office365.com/EWS/Exchange.asmx Email Address: <firstname>.<lastname>@yourcompany.tld Login User Name: <firstname>.<lastname>@yourcompany.tld
- Adressbook/Calendar
- Plugins: "TbSync" and "Provider for Exchange ActiveSync"
- If not already present, install the "Lightning" plugin (already included in Thunderbird >60), afterwards install the plugins mentioned above with the help of the add-ons-manager in Thunderbird.
- 'Configure the calendar sync:'
- Edit → Synchronisation Settings (TBSync)
- Select "Account Actions" in the following dialog-box, "+ Add new account" and "Exchange ActiveSync" afterwards
- Now fill in your Exchange (o365) settings:
Server configuration: Automatic configuration via ActiveSync Account name: <feel-free-to-choose-one> User name (email address): <firstname>.<lastname>@yourcompany.tld Password: <your password>
Those steps are described in this systutorial howto link , too.
- Additional Addons/plugins (my personal recommendation)
- Enigmail (OpenPGP encryption)
- Foxclocks (display different timezones)
- Quicktext (create/insert text templates with shortcuts)
- Unmangle Outlook Safelinks (disable those unreadable o365 safelinks)
Office (text/spreadsheet/presentation/...)
- Libreoffice
- Install Libreoffice with your package manager.
- Libreoffice consists of Base/Calc/Draw/Impress/Writer, if you are familiar with MSOffice you can compare it to Access/Excel/PictureManager/Powerpoint/Word.
- You can also export every Libreoffice document from within the Application to pdf without any additional tool.
- Documents are saved in the open document format (odf) as default but you can open/save MS-Office documents (eg. doc/docx), too.
- Here's what Libreoffice Calc (comparable to Excel) looks like:
-
Calc
- There's pdf support right out of the box on most Linux distributions (pdf viewer, pdf printer) so there's no need to install Adobe pdf reader or any additional pdf printer.
- If you're looking for an pdf-editor, the application "Master PDF Editor" might be the right choice for you, download (tar.gz/.deb/.rpm) is available at Master pdf editor
- Btw, this software is available for MS-Windows, too. Keep in mind that it's only free for non-commercial usage.
- Dia
- Install dia-gnome with your package manager
- You can create flow-charts, network diagrams, UML with dia.
- Lucidchart
- If you're NOT concerned about privacy you could try Lucidchart which is a web based network, etc diagram solution and very well comparable&compatible to Visio.
- There's also an integration possible with Atlassian products like Jira and Confluence!
- Screenshot
- As the name already tells, this tool is for screenshots, it's already installed in Fedora (Gnome3)
- Shutter
- With shutter you can make screenshots and manipulate/edit them afterwards.
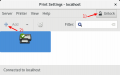
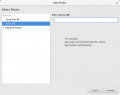
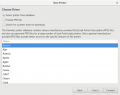
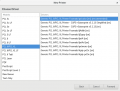
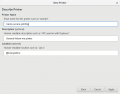
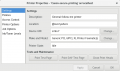
Printing
- CUPS
- Tired of the printer driver install hell? Here's how it looks like in Linux...
- In Linux the CUPS daemon is used for printing.
- If you're company/university/etc. uses a Uniflow printing method with an SMB share, this might fit your needs:
URI: smb://<company-smb-printer-fqdn>/printer-share-directory Printertype: Generic PCL 6/PCL XL Printer Foomatic/pxlcolor (recommended)
- And yes, you know it already, ask the friendly printer gurus at your company/university for the FQDN and printer share details ;-)
- Step by step howto
- When printing a document you have to authenticate yourself with your credentials (a dialog window will pop-up for this)
- After that you can get the print job at your preferred Uniflow printer.
Remote desktop client (RDP/...)
- Remmina
- Install remmina with your package manager.
- With Remmina you can configure your RDP connections. You have the ability to define different groups, set different screen resolutions/color depth and so on.
- This might be helpful if there are applications which are only available for Windows.
- Alternatives
- xfreerdp
- rdesktop
Scanning
This is only relevant when using scanners locally connected to your laptop/desktop.
- Simple Scan
- Install 'simple-scan' with your package manager, it's a lightweight tool to get easy scanning access and it works with most scanner models.
VDI
Virtual machines
Web
Backup/Restore
Todo...